Our Products
Lead Acid Batteries
Lead Acid batteries remain one of the most widely used energy storage solutions for UPS, inverter, and backup power systems, especially in applications where initial cost, availability, and proven reliability are key decision factors. Despite newer technologies entering the market, Lead Acid batteries continue to play a critical role in residential, commercial, and industrial backup systems due to their simple operating principle, high surge capability, and ease of replacement. When correctly selected and maintained, they offer dependable performance for predictable backup requirements.
Why Lead Acid Still Matters
- Cost-effective and readily available, especially for standard backup scenarios.
- Reliable with mature technology that has been proven over decades.
- Highly recyclable, making them one of the most recycled battery technologies globally.
Despite the rise of advanced battery chemistries (like LFP), Lead Acid batteries continue to hold a significant share in UPS and energy storage markets because they are:
This broad applicability makes lead-acid batteries a practical component in many legacy and current energy storage systems.
WHY LEAD ACID BATTERIES ARE STILL WIDELY USED
Lead Acid batteries continue to be widely deployed because they combine proven reliability
with simplicity of operation. Unlike advanced lithium systems, Lead Acid batteries follow a
straightforward electrochemical process, making them easier to install, service, and
troubleshoot, especially in locations with limited technical support. For many users,
especially in cost-sensitive projects or locations with limited technical support, Lead Acid
batteries remain a practical and proven solution.
For many users, especially in cost-sensitive projects or where local maintenance
infrastructure is limited, Lead Acid batteries remain a practical, robust, and cost-effective
energy storage solution.
Lead acid -commercial & Indus application
HOW TO CALCULATE BATTERY SIZING FOR HOME USE
Correct battery sizing ensures reliable power backup, optimal performance, and longer battery life. Battery capacity is determined based on connected load, backup duration, system voltage, and usable depth of discharge (DoD).
- Step 1: Calculate Total Connected Load (Watts)
List all appliances you want to run during a power cut and add their wattage.
Example: BLDC Fans – 3 × 35 W LED Lights – 6 × 20 W Television – 120 W Wi-Fi Router & Charging – 100 W Total Load ≈ 445 W. - Step 2: Decide Required Backup Time (Hours)
Choose how long you want backup during a power failure.
Example: 4 hours - Step 3: Calculate Total Energy Required (Watt-hours) Total Energy (Wh) = Load (W) × Backup Time (h) 445W × 4 h = 1780 Wh
- Step 4: Account for Inverter Efficiency Inverters are not 100% efficient. Typical efficiency ranges from 85–95%. Adjusted Energy = 1780 Wh ÷ 0.85 ≈ 2094 Wh
- Step 5: Apply Depth of Discharge (DoD)
Depth of Discharge indicates how much of the battery capacity can be safely used.
• Lead Acid Battery DoD: ~50% • LFP Battery DoD: 80–90% For Lead Acid: Required Battery Energy = 2094 Wh ÷ 0.50 ≈ 3560 Wh - Step 6: Convert Energy to Battery Capacity (Ah)
Battery Capacity (Ah) = Required Wh ÷ Battery Voltage
For a 12V system: 3560 Wh ÷ 12 V ≈ 296 Ah
LEAD ACID BATTERIES FOR HOME UPS
Lead Acid batteries are commonly used in home UPS systems due to their affordable
upfront cost and simple integration with standard inverter setups. They are particularly
suitable for households looking for basic backup during short power cuts without significant
system complexity.
Lead Acid batteries are preferred for home applications as they provide better durability and
longer life compared to flat plate batteries, especially under frequent power interruptions.
However, correct sizing, ventilation, and periodic maintenance are essential to ensure
consistent performance and extended battery life.
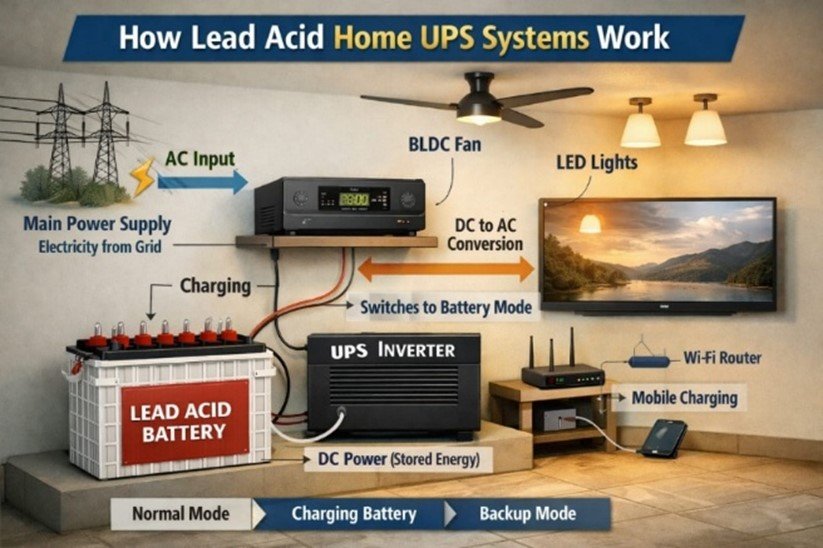
- Lighting and ceiling fans: Provides steady power for lights and fans to maintain comfort during outages.
- Television and entertainment systems: Keeps TVs, set-top boxes, and speakers operational without flicker or shutdowns.
- Networking and communication equipment: Ensures Wi-Fi routers, modems, and VOIP systems stay connected for uninterrupted internet access.
- Computers and home office gear: Allows safe shutdown or ongoing work during brownouts and short outages.
HOW LEAD ACID HOME UPS SYSTEMS WORK
APPLICATIONS:
Residential & Home UPS Systems
Lead Acid batteries are commonly used in home UPS systems to deliver dependable backup power when grid supply fails. They are especially effective in households where short-to- moderate backup duration is sufficient, and cost efficiency is a priority.
Typical uses include:
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. How does depth of discharge affect Lead Acid battery life?
Lead Acid batteries perform best when operated within a limited depth of discharge. Frequent deep discharging accelerates plate degradation and sulfation. For longer battery life, UPS systems are typically designed to limit discharge to moderate levels rather than draining the battery fully during every power cut.
2. Why are tubular Lead Acid batteries preferred for home UPS systems?
Tubular batteries use reinforced positive plates that reduce active material shedding during repeated charge–discharge cycles. This makes them more reliable for homes with regular power interruptions compared to flat plate batteries, which are better suited for occasional backup needs.
3. What role does charging control play in Lead Acid battery performance?
Proper charging voltage and current regulation are critical. Incorrect charging can lead to sulfation, excessive water loss, or overheating. A well-matched UPS or inverter ensures correct float and boost charging, directly improving battery efficiency and lifespan.
4. How do frequent short power cuts impact Lead Acid batteries?
Repeated short outages can prevent the battery from reaching full charge, causing partial state-of-charge operation. Over time, this leads to capacity loss and reduced backup performance. Correct battery sizing and adequate recharge time help mitigate this issue.
5. Can Lead Acid batteries be effectively used in solar-assisted UPS systems?
Yes. Lead Acid batteries are commonly used in solar-based UPS and off-grid systems. However, charge controller settings must be accurately configured to avoid overcharging or deep discharge, both of which can significantly reduce battery life
- Server rooms and networking closets: Helps prevent data loss by bridging gaps until generators take over or power is restored.
- Retail outlets & office UPS systems: Keeps POS machines, billing systems, and lighting operational.
- Telecommunication backup: Widely deployed to maintain uptime of telecom base stations, critical for 24/7 connectivity.
- Small industrial control rooms: Provides stable backup for PLCs, sensors, and automation panels during grid instability.
LEAD ACID BATTERIES FOR COMMERCIAL & INDUSTRIAL UPS
In commercial and industrial environments, Lead Acid batteries are widely used in UPS systems for offices, telecom sites, control rooms, and backup infrastructure where predictable backup duration and known load behaviour are required. They are particularly suitable for applications where backup is occasional rather than continuous, and where maintenance teams are available to manage battery health.
APPLICATIONS:
Commercial & Business Backup
In commercial environments, Lead Acid batteries are a cornerstone of UPS systems that protect critical electronics and business continuity. Their ability to deliver high surgecurrents and reliable voltage during short outages makes them suitable for a variety ofbusiness uses.
Key commercial applications:
HOW LEAD ACID OMMERCIAL & INDUSTRIAL UPS SYSTEMS WORK

Examples include:
- Solar energy storage systems:Stores excess solar power for use during low generation periods or outages in off-grid and hybrid green energy systems.
- Wind energy storage support: Works in tandem with variable input sources to smooth output and support grid-tie systems.
- Emergency lighting & safety systems: Provides stored energy to emergency lights, alarms, and exit signs in commercial buildings.
Other Practical Uses
Lead Acid batteries are also found in several non-UPS applications due to their high reliability, recyclability, and cost efficiency:
- Automotive starting, lighting, and ignition (SLI): Powers vehicle electrical systems and starter motors.
- Marine and RV auxiliary systems: Provides auxiliary power in boats and recreational vehicles.
- Material Handling & Motive Power: Lead Acid batteries are widely used in electric forklifts, industrial lift trucks, and warehouse handling equipment due to their ability to deliver high traction current, withstand deep discharge cycles, and operate reliably in demanding environments. In locomotive and rail systems, they support engine starting, control circuits, signalling, and emergency backup functions. Additionally, Lead Acid batteries continue to play a critical role in telecom infrastructure, providing dependable standby power for base stations and communication networks, particularly in large-scale and remote installations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Are Lead Acid batteries suitable for commercial UPS systems with frequent power
events?
Lead Acid batteries are suitable for standby and intermittent UPS applications, where power outages are occasional and predictable. For environments with frequent or prolonged outages, careful charge management and controlled depth of discharge are essential to prevent accelerated battery wear.
2. How do I calculate the right Lead Acid battery capacity for my UPS?
Battery sizing is done by listing the actual loads you want to run during power cuts—such as lights, BLDC fans, TV, and plug points—and adding their wattage. Based on the required backup time, the battery Ah capacity is selected so the system operates without deep discharge. Proper sizing helps maintain voltage stability, prevents overload, and improves battery life.
3. What hidden operational costs should industries consider with Lead Acid batteries?
Although initial investment is lower, long-term operational costs may increase due to routine maintenance, electrolyte management, higher floor space requirements, ventilation infrastructure, and more frequent battery replacement compared to advanced chemistries.
4. Can Lead Acid UPS battery banks be expanded for growing industrial loads?
Yes, expansion is possible by adding parallel battery strings. However, scalability is limited by physical space, weight, ventilation needs, and battery string balancing, which become critical factors in medium to large industrial installations.
5. What happens if a Lead Acid battery is undersized or oversized for a UPS?
If a Lead Acid battery is undersized, it will discharge too quickly, causing voltage drops and reducing backup time and battery life. If oversized, the system works safely but charging time increases and available capacity may not be fully utilized. Correct sizing ensures balanced charging, stable performance, and optimal battery lifespan.

Lead acid Residential home ups

Lead acid Residential home ups

Lead acid Residential home ups

Lead acid -commercial & Indus application

Lead acid -commercial & Indus application

Lead acid -commercial & Indus application



